Sql Ystem-generated Primary Key That Is Usually Hidden From Users
SQL PRIMARY KEY Constraint
- Sql System-generated Primary Key That Is Usually Hidden From Users 2017
- Sql Ystem-generated Primary Key That Is Usually Hidden From Users Name
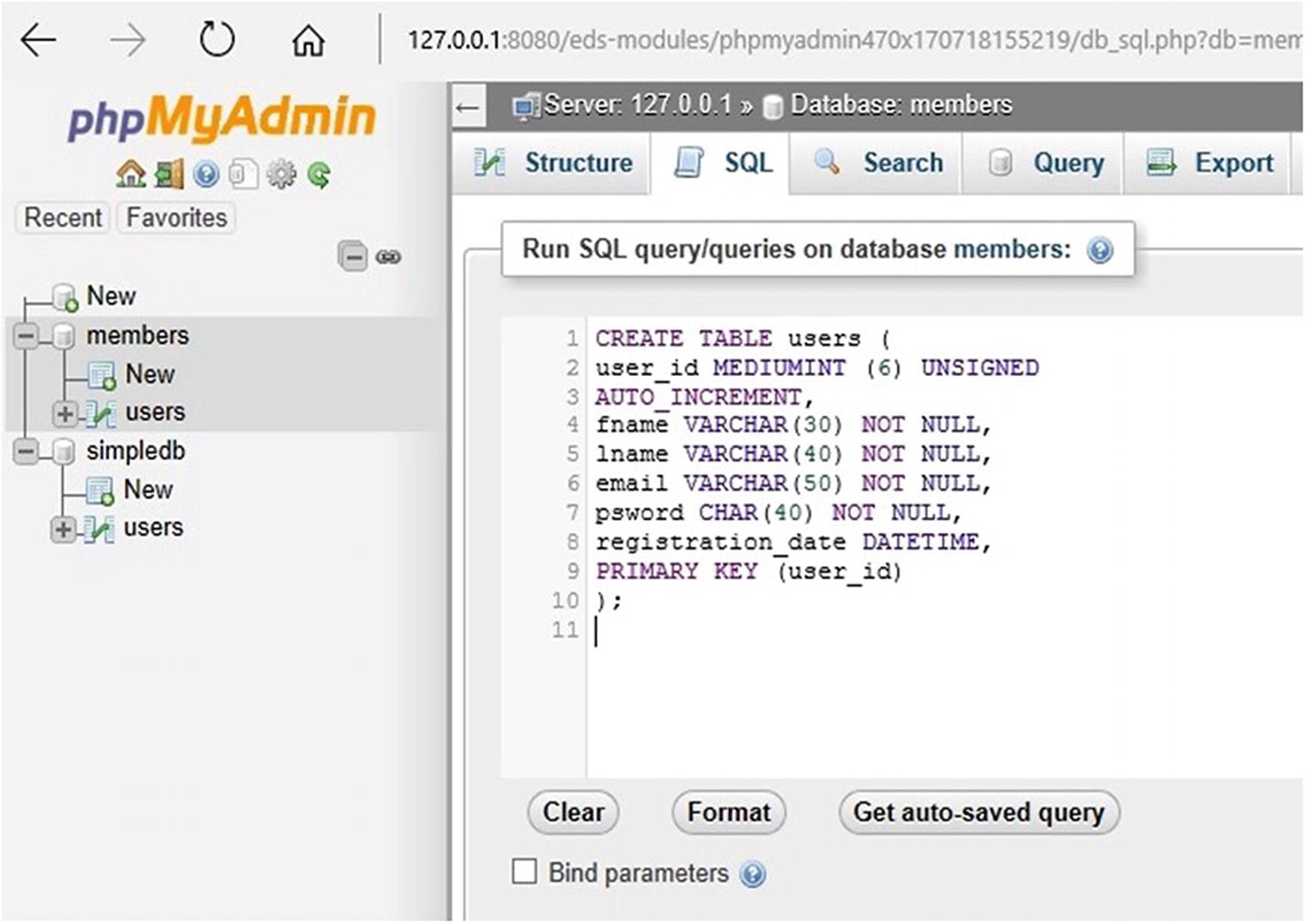
What is Primary Key in SQL? A primary key is defined as the single column or a set of columns that uniquely identifies each row in the table. As soon as one primary key constraint is defined for the table, the database engine automatically creates a unique index for the primary key column.
The PRIMARY KEY constraint uniquely identifies each record in a table.
Primary keys must contain UNIQUE values, and cannot contain NULL values.
Sql System-generated Primary Key That Is Usually Hidden From Users 2017
Values have no meaning to users and are usually hidden on forms, queries and reports. A surrogate key is often used in place of a composite primary key. Referential integrity states that every value of a foreign key must match a value of an existing primary key. Ubuntu generate ssh key with email. Primary keys are unique identifiers in SQL. The quiz includes questions about how primary keys are used, primary key requirements and primary keys that would be relevant to certain types of. Jul 17, 2009 When Information Schema is used, we will not be able to discern between primary key and foreign key; we will have both the keys together. In the case of sys schema, we can query the data in our preferred way and can join this table to another table, which can retrieve additional data from the same.
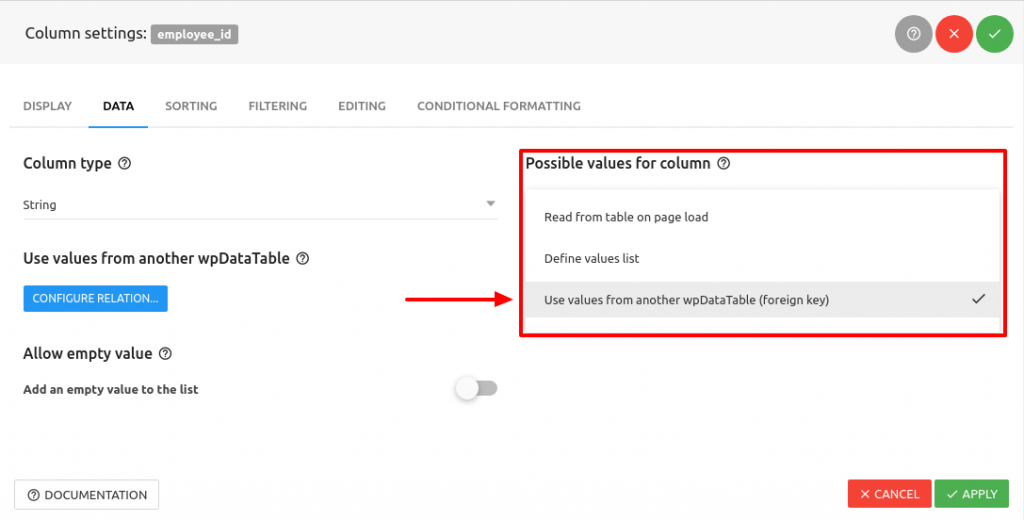
A table can have only ONE primary key; and in the table, this primary key can consist of single or multiple columns (fields).
SQL PRIMARY KEY on CREATE TABLE
The following SQL creates a PRIMARY KEY on the 'ID' column when the 'Persons' table is created: Erlang public and private key generator.
MySQL:
ID int NOT NULL,
LastName varchar(255) NOT NULL,
FirstName varchar(255),
Age int,
PRIMARY KEY (ID)
);
SQL Server / Oracle / MS Access:
ID int NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY,
LastName varchar(255) NOT NULL,
FirstName varchar(255),
Age int
);
To allow naming of a PRIMARY KEY constraint, and for defining a PRIMARY KEY constraint on multiple columns, use the following SQL syntax:
MySQL / SQL Server / Oracle / MS Access:
ID int NOT NULL,
LastName varchar(255) NOT NULL,
FirstName varchar(255),
Age int,
CONSTRAINT PK_Person PRIMARY KEY (ID,LastName)
);
Note: In the example above there is only ONE PRIMARY KEY (PK_Person). However, the VALUE of the primary key is made up of TWO COLUMNS (ID + LastName).
SQL PRIMARY KEY on ALTER TABLE
To create a PRIMARY KEY constraint on the 'ID' column when the table is already created, use the following SQL:
MySQL / SQL Server / Oracle / MS Access:
To allow naming of a PRIMARY KEY constraint, and for defining a PRIMARY KEY constraint on multiple columns, use the following SQL syntax:
MySQL / SQL Server / Oracle / MS Access:
ADD CONSTRAINT PK_Person PRIMARY KEY (ID,LastName);
Note: If you use the ALTER TABLE statement to add a primary key, the primary key column(s) must already have been declared to not contain NULL values (when the table was first created).
DROP a PRIMARY KEY Constraint
To drop a PRIMARY KEY constraint, use the following SQL:
MySQL:
Sql Ystem-generated Primary Key That Is Usually Hidden From Users Name
SQL Server / Oracle / MS Access: